

The dorsal interossei muscle abducts at the metacarpophalangeal joint. Attaches to the sides of the metacarpals and base of the proximal phalanx and dorsal digital expansions ( Figure 33-2C). Medial two tendons of flexor digitorum profundusĭorsal digital expansions and base of proximal phalanges of digits 2–4Ībducts digits (DAB) and flexes metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal jointsĭorsal digital expansions and base of proximal phalanges of digits 2, 4, and 5Īdducts digits (PAD) and flexes metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Lateral sides of dorsal digital expansions for digits 2–5įlexes metacarpophalangeal joints and extends interphalangeal joints Lateral two tendons of flexor digitorum profundus Pisiform bone, pisohamate ligament, and tendon of flexor carpi ulnarisįlexion of metacarpophalangeal joint of digit 5 Oblique head: metacarpals 2 and 3 and capitate Medial rotation of thumb and flexion of metacarpal of digit 1
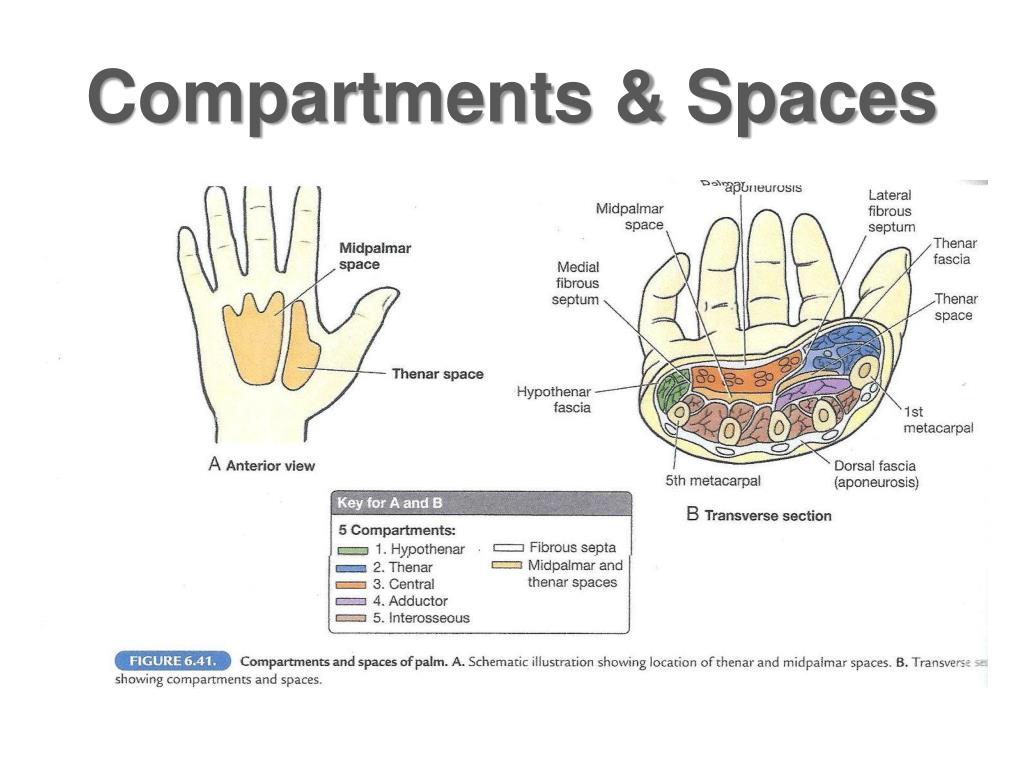
#HAND COMPARTMENTS SKIN#
Tenses the skin over the hypothenar musclesįlexor retinaculum, scaphoid, and trapeziumĭeep head: trapezium and flexor retinaculumįlexion of digit 1 (metacarpophalangeal joint) Palmar aponeurosis and flexor retinaculum Because of the attachment of the muscles and the location of the hood, the small intrinsic muscles will produce flexion at the metacarpophalangeal joint while extending the interphalangeal joints. The small intrinsic muscles that attach laterally are responsible for delicate finger movements that would not be possible with the extensor digitorum, flexor digitorum superficialis, and profundus muscles alone.

Laterally, the lumbricals and the dorsal and palmar interossei muscles attach. Proximally and centrally, the extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi, extensor indicis, and extensor pollicis brevis muscles attach to the dorsal digital expansion. An aponeurosis covering the dorsum of the digits and attaches distal to the distal phalanx. The extensor retinaculum works to retain the tendons that are near the bone while allowing proximal and distal gliding of the tendons ( Figure 33-1B). Continuous with the fascia of the forearm and attached laterally to the radius and medially to the triquetrum and pisiform bones. This ligament should not be confused with the flexor retinaculum, which is located deeper to the transverse palmar ligament. Continuous with the extensor retinaculum from the dorsal side of the wrist and wraps around, anteriorly, to form a fascial band around the flexor tendons. Laterally, the flexor retinaculum is anchored to the scaphoid and trapezium. The flexor retinaculum anchors medially to the pisiform and the hook of the hamate.
The median nerve and the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and flexor pollicis longus muscles, and their associated synovial sheaths, pass through this tunnel.
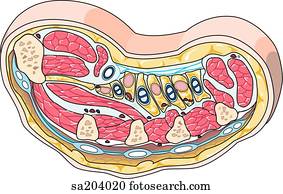
Forms a roof over the concavity created by the carpal bones, forming a tunnel (i.e., the carpal tunnel).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
